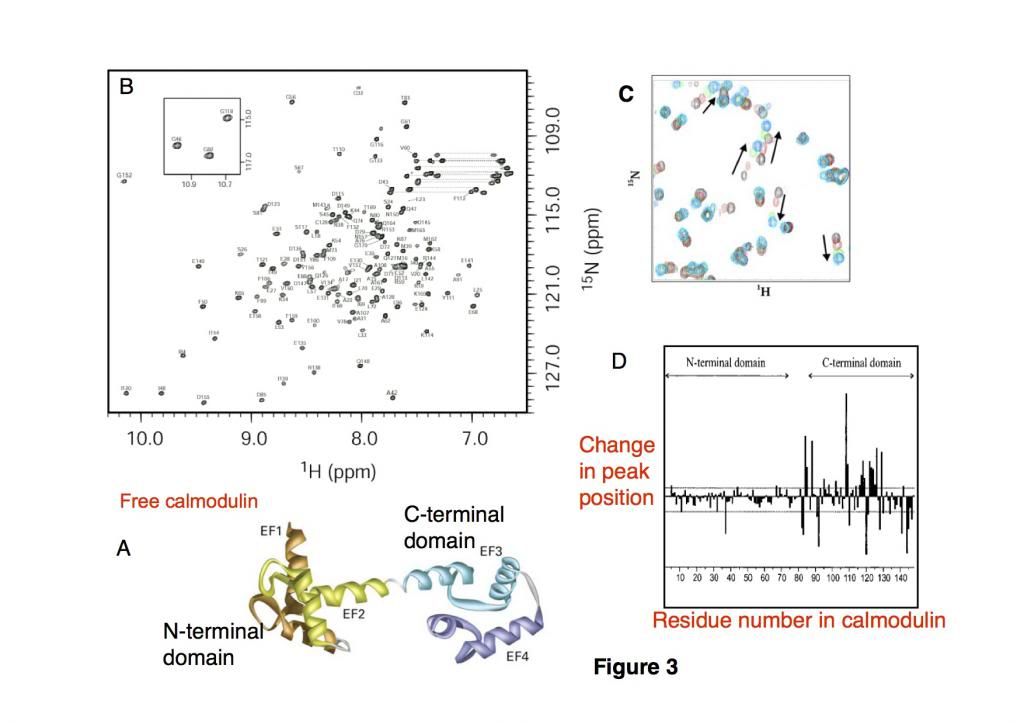
Calmodulin (CaM), a 16.7kDa EF-hand regulatory calcium-binding protein composed of two domains (Figure 3A) and mediates a range of cellular processes, undergoes a conformational change upon binding to Ca2+ ions, which enables it to bind to specific proteins. The resonances observed in the fingerprint of CaM have been assigned (Figure 3B) to their specific residue in the CaM sequence, which allows us to know which cross-peak in this 148 residue protein corresponds to an amino acid within the protein.
In this experiment, a 25 amino acid peptide substrate was bound to calmodulin in different ratios of CaM: peptide = 1:0, 1:0.5, 1:0.8, 1:1.2 and HSQC spectra were recorded for each sample (Fig 3C) (black= 1:0, red = 1:0.5, green 1:0.8 and cyan 1:1.2).
We can measure the changes in the positions of the cross-peaks for each of the amino acids within the calmodulin during the titration and plot this (figure 3D)
Using these data and the figures, describe what structural changes occur in CaM when the peptide binds. (5 marks total)