I got stuck somehow when I tried to understand the difference between the equivalence point and neutralization point through a specific example.
Just to get this clear, the theoretical definitions seem clear to me. EP: n (HA) = n (A-) which also means n (H3O+) = n (OH-)
Neutralization point: PH value = 7
But I somehow can't wrap my mind around it when trying to apply it to reaction equation, like this one
CO3HOO- + H3O+ + Na- + OH-
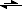
CO3HOO- + NA- + 2H20
What I don't understand here is that at the EP n (Na-) = n (CO3HOO-) which also means n (H30+) = n (OH-) which actually means that the balance is all to the right side of the equation.
But why is the PH value not = 7 here anyways ? Is it because CO3HOO- is still in there and could take an H from H20, so that it's PH value is at around 6 at the EP ?