Due to lack of time, I was unable to finish, now the
edit function is unavailable, so I will continue here.
Sulfuric acid ionizes like this: H
2SO
4 +H
2O
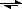
H
3O
+ + HSO
4. The resulting bisulfate ion ionized again - but to a much smaller extent: HSO
4 + H
2O
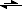
H
3O
+ + SO
4.
Thus, with a nitrate salt: H
2SO
4(aq) + XNO
3(s/aq) → HNO
3(g) + XHSO
4(s/aq).
With considerable heating, the volatility of nitric acid over X-bisulfate causes the reaction to go further to completion. Heating to this temperature cause much decomposition to the nitric acid: 2 HNO
3 → H
2O + 2 NO
2 1/
2 O
2. This reaction is mostly irreversible. Some of the NO
2 might dissolve in the nitric acid, but it won't be oxidized to the
+5 oxidation state. This acid is called RFNA or red fuming nitric acid. You can oxidize the dissolved NO
2 (or at lower temperatures, more correctly called N
2O
4) by adding concentrated hydrogen peroxide to the solution, or bubbling dry air or oxygen through it. When nitric acid is free of N
2O
4, it will become colorless, an excellent indicator.